Goshen Network: Revolutionizing Layer 2 Solutions on Ethereum
Ethereum is the largest smart contract network in the world. The blockchain hosts most of the DeFi and NFT markets. Unfortunately, the large scale often causes congestion and high transaction fees. Many projects are trying to solve this problem by creating so-called Layer 2 protocols. One is the Goshen Network, which we’ll focus on in today’s article. We’ll explain what it is, how it works, what sets it apart from the competition, and much more. But let’s start with the basics, i.e., explaining what Layer 2 is and why it is needed. So, let’s get started!

Article contents
What Is Layer 2?
Layer 2 is a scaling solution that aims to offload transactions from the core network by moving them off-chain, meaning off the project’s blockchain being scaled.
L2 solutions are designed to provide the fastest possible transaction speeds while reducing transaction costs. In most cases, security is provided by layer one – often referred to as the base layer.
The most common chain using such solutions is Ethereum. It is scaled by many projects (including Goshen Network), each using different solutions and technologies. However, more than just the largest smart contract platform needs it. Bitcoin also has its own L2 solution, which is the Lightning Network.
Scaling Solutions in Layer 2
Layer 2 solutions mainly work in three different ways. These are:
- Rollups
- Sidechains
- Channels
Each of them has its advantages and disadvantages. However, all of them have the same goal. They want to speed up transactions while reducing fees.
Rollups combine many different transactions into one. Then, later, deposit them back into the original chain. They are thus a second layer built on top of Layer 1. An example using rollups, specifically optimistic rollups, is Goshen Network.
Unlike rollups, sidechains are completely separate blockchains. They connect and transmit transactions to the Layer 1 network at once. A sidechain can be compared to a bridge that connects two blockchains. The most popular example of an Ethereum sidechain is Polygon.
Channels track multiple payments between two users, similar to rollups. However, there is one key difference. They only record two transactions on the main network. What does this mean? Assume you send ten dollars back and forth 20 times. In that case, the rollup would have to register as many as 20 transactions. In the case of channels, only the final amount held by each user is added to Layer 1. Lightning Network, the most popular Bitcoin scaling solution, is an example of this scaling method.
What Is Goshen Network, and How Does It Scale Ethereum?
Goshen Network uses optimistic rollup technology to scale Ethereum. Doing so can reduce gas costs while keeping the base chain decentralized and secure.
Goshen Network has an interesting feature that sets it apart from other similar projects. It is a so-called RISC-V machine. Its calculations are made through it, and in case of problems, a prune fraud state can be easily performed in the RISC-V-Chain program.
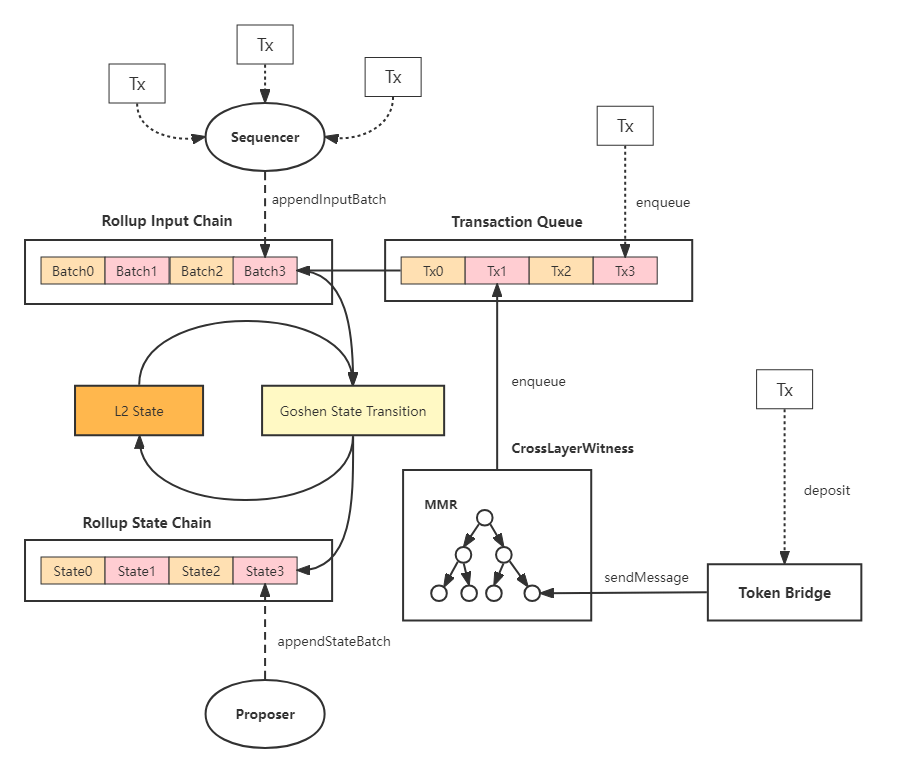
This Layer 2 blockchain is built in a layered architecture divided into a bottom and an upper layer. The bottom layer contains a general-purpose computing environment based on RISC-V. It’s the one that migrates Layer 1 calculations off-chain and ensures full compatibility with Ethereum’s Layer 1 ecosystem.
In addition, there is also a cross-layer communication system. It ensures interoperability between the two layers and the operation of upper-layer applications – such as the token bridge.
Goshen Network’s Gas Fees
When it comes to gas fees, Goshen Network wants to reduce them by 100 times compared to Ethereum. How? The sequencer simply accepts only those transactions whose gas price is higher than 1/100 of the ETH blockchain gas price.
In general, the Goshen Network gas fee consists of two parts:
- Transaction execution: this fee is the same as Layer 1. It is used to pay for the computation and storage consumed during the execution of smart contracts.
- Data publishing: the sequencer collects data and publishes it on Layer 1 in parts. This fee is paid by those making the transactions. For transactions sent directly from Ethereum to Goshen Network’s Layer 2, there is no need for the sequencer. Thus, there is no need to pay a fee for data publication.
Goshen Network Is Developer-Friendly
Goshen Network is a developer-friendly Layer 2 solution. Why? Because there is no rocket science involved. Developers can easily migrate dApps from Layer 1 and create new ones using the same dev skills and tools as in the case of Ethereum.
Deploying a dApp on Goshen can be done using any Ethereum smart contract development framework, such as:
- Hardhat
- Foundry
- Truffle
- Brownie
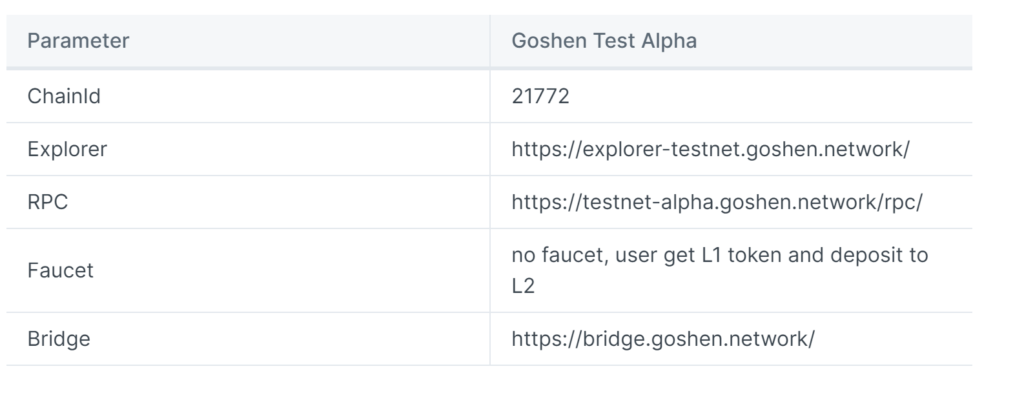
The only change you need to make is to edit the RPC settings for the Goshen Network (as shown in the image below).
Bitcoin EVM Layer
The Ordinals project and the BRC-20 standard also inspired the Goshen team. As a result of this inspiration, they created a new proposal. What kind? It’s about integrating the Ethereum virtual machine (EVM) execution layer into the Bitcoin network.
According to the developers, such a solution has many advantages, including:
- Utilizing SegWit, thus reducing dApp fees compared to the Ethereum blockchain.
- Streamlining data transfer will eliminate the need for two separate transactions (commit and reveal).
- Eliminating the need to split transactions (as in BRC-20), even for basic transfers.
- Offer seamless compatibility with the Ethereum ecosystem. This eliminates the need to create new tool sets.
Follow us on Medium, Twitter, Telegram, YouTube, and Publish0x to stay updated about the latest news on StealthEX.io and the rest of the crypto world.
Don’t forget to do your own research before buying any crypto. The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author.
crypto world cryptocurrency Ethereum Goshen Goshen NetworkRecent Articles on Cryptocurrency
 Toshi Price Prediction: Will TOSHI Coin Reach $1?
Toshi Price Prediction: Will TOSHI Coin Reach $1?  GoPlus Security Price Prediction: Will GPS Coin Reach $1?
GoPlus Security Price Prediction: Will GPS Coin Reach $1? 
